(Radiology Review) Multidetector-row CT enables the identification and assessment of the right adrenal vein in most patients, according to Dr. Tomonori Matsuura and colleagues at Tohoku University Graduate School of Medicine in Sendai, Japan.
Secondary hypertension is often caused by primary aldosteronism. Unilateral aldosterone-producing adenoma and bilateral idiopathic hyperaldosteronism are the two most common causes, and adrenal vein sampling is used for differentiation.
Catheterization for adrenal venous sampling remains a challenge because of narrow vessel diameter and variable anatomy, including orifice position along the inferior vena cava (IVC) and takeoff direction, according to the researchers, whose study was published in the American Journal of Roentgenology (August 2008, Vol. 191:2, pp. 402-408).
Using an eight-slice scanner (Aquilion, Toshiba Medical Systems, Tokyo), the researchers obtained axial and multiplanar images of the right adrenal vein with contrast-enhanced MDCT in 104 patients with thoracoabdominal vascular disease. They evaluated "degree of visualization; relationship to accessory hepatic or other veins; anatomy, including location of the orifice in relation to the surrounding structures; direction from the inferior vena cava; and length and diameter."
The following MDCT parameters were used: 0.5 seconds per rotation, 1-mm collimation, 14 mm/sec table increment (pitch, 7.0), tube voltage of 120 kV, and tube current of 350 mA. Immediately prior to scanning, an injection of 100 mL of contrast material containing 300 mg I/mL (Iopamiron, Bayer Schering Pharma, Berlin, Germany) was administered through the antecubital vein at 3.5 mL/sec.
With respect to the vertical position along the IVC, the right adrenal vein orifice was "craniocaudally located between the level of vertebrae T11 and L1" with 69% joining the IVC from the "middle third of T12 to the superior third of L1," according to the authors. The right adrenal vein took a caudal direction in 89% of patients and a cranial direction in 11%. "The transverse direction from the inferior vena cava was posterior and rightward in 56 patients (77%) and posterior and leftward in 17 (23%)," the authors wrote.
The average right adrenal vein length was 3.8 mm and the average diameter was 1.7 mm, they reported.
"Radiologic Anatomy of the Right Adrenal Vein: Preliminary Experience with MDCT"
Tomonori Matsuura et al
Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Tohoku University Graduate School of Medicine, 1-1 Seiryo, Aoba, Sendai, Miyagi, 980-8574, Japan
AJR 2008 (August); 191:402-408
By Radiology Review
September 17, 2008
Copyright © 2008 AuntMinnie.com






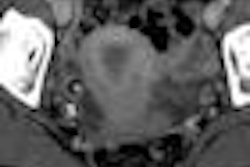
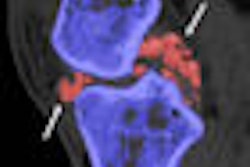






![Images show the pectoralis muscles of a healthy male individual who never smoked (age, 66 years; height, 178 cm; body mass index [BMI, calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared], 28.4; number of cigarette pack-years, 0; forced expiratory volume in 1 second [FEV1], 97.6% predicted; FEV1: forced vital capacity [FVC] ratio, 0.71; pectoralis muscle area [PMA], 59.4 cm2; pectoralis muscle volume [PMV], 764 cm3) and a male individual with a smoking history and chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder (COPD) (age, 66 years; height, 178 cm; BMI, 27.5; number of cigarette pack-years, 43.2, FEV1, 48% predicted; FEV1:FVC, 0.56; PMA, 35 cm2; PMV, 480.8 cm3) from the Canadian Cohort Obstructive Lung Disease (i.e., CanCOLD) study. The CT image is shown in the axial plane. The PMV is automatically extracted using the developed deep learning model and overlayed onto the lungs for visual clarity.](https://img.auntminnie.com/mindful/smg/workspaces/default/uploads/2026/03/genkin.25LqljVF0y.jpg?auto=format%2Ccompress&crop=focalpoint&fit=crop&h=112&q=70&w=112)