German researchers using CT have examined a 17th century mummy of a 1-year-old boy found in the crypt of an Austrian aristocratic family, according to a report published October 26 in Frontiers in Medicine.
What they found checks out with researchers' current understanding of how children were raised in Europe during the Renaissance era, study lead author Andreas Nerlich, PhD, of the Academic Clinic Munich-Bogenhausen, told AuntMinnie.com.
"Aristocratic infants of that period were kept somewhat 'hidden' in houses or castles to avoid contact with the 'normal' environment, such as sunlight and perhaps even ordinary people," he said.
Nerlich and colleagues investigated the crypt's history, finding that it was used by the Counts of Starhemberg, who buried their wives and first-born sons there. The child was buried around 1600 A.D. and was likely Reichard Wilhelm, named for his grandfather Reichard von Starhemberg. Conditions in the crypt caused his body to mummify naturally. He was laid to rest clothed in a silk coat in an unmarked wooden coffin and was the only unidentified body in the crypt, the researchers noted.
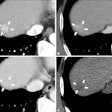
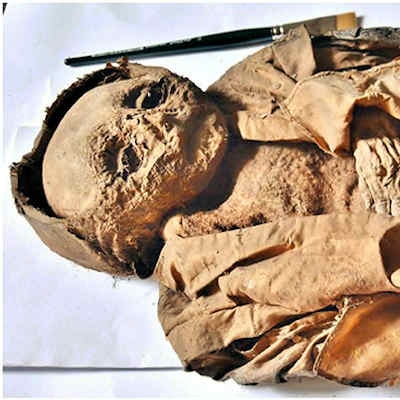
 The infant mummy of the Hellmonsödt crypt in Austria. Overview of the complete body in a silk coat. Images courtesy of Andreas Nerlich et al.
The infant mummy of the Hellmonsödt crypt in Austria. Overview of the complete body in a silk coat. Images courtesy of Andreas Nerlich et al.Nerlich's group used CT to conduct a virtual autopsy, measuring the boy's bone lengths and assessing his lungs. The team also performed radiocarbon testing.
The child's soft tissue showed that he was overweight for his age. But his ribs had a malformation pattern called rachitic rosary, which is often caused by rickets or scurvy.
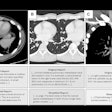
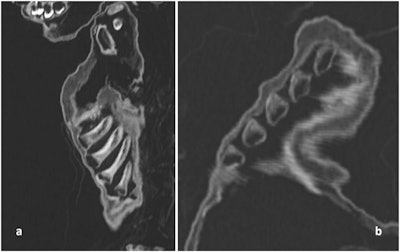 CT scan of the costochondral junction with an enlargement such as seen in "rickety rosary" but also in "scurvy rosary." (a) Sagittal section; (b) oblique section.
CT scan of the costochondral junction with an enlargement such as seen in "rickety rosary" but also in "scurvy rosary." (a) Sagittal section; (b) oblique section."The combination of obesity along with a severe vitamin-deficiency can only be explained by a generally 'good' nutritional status along with an almost complete lack of sunlight exposure," Nerlich said in the journal statement. "We have to reconsider the living conditions of high aristocratic infants of previous populations."
CT also showed pleural adhesions in the baby's right lung, suggesting that he had pneumonia -- an illness to which children suffering from rickets are more vulnerable -- and which may have contributed to his death, the team noted.