Adding radiomics to a CT-feature deep-learning model outperforms the CT model alone for preoperatively predicting visceral pleural invasion (VPI) in patients with early-stage non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), researchers have reported.
The study results could improve patient care, wrote a team led by Qinyue Luo, MD, of Huazhong University of Science and Technology in Wuhan, China.
"The contrast-enhanced CT-based radiomics model [appears] valuable for optimizing clinical decision-making," the group noted. The findings were published January 26 in Insights Into Imaging.
VPI is a "high-risk pathological factor for recurrence, and patients with VPI may benefit from postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy," the authors explained. But having to wait for postoperative pathologic confirmation of VPI can delay treatment decisions. To investigate a way to preoperatively improve the diagnostic process, the team developed three deep-learning models and tested them with a cohort of 523 NSCLC patients with clinically staged, IA disease who underwent surgery between December 2019 and June 2022.
Of the total patient cohort, 195 individuals had visceral pleural invasion, and 328 did not. The three models included a CT-feature model (consisting of 13 morphological features that measured tumor relationship to the pleura and its density, maximum diameter, and spiculation), a radiomics model (which included 10 features), and a combined model. Patients were randomized into training, validation, and testing sets.
Luo and colleagues segmented regions of interest semi-automatically using deep learning and applied least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression to certain radiomics features. Finally, they evaluated the performance and clinical utility of the models using the area under the curve (AUC) measure.
The group found that the combined radiomics and CT-feature model had the highest AUC in the test set.
Performance of three different models for preoperatively predicting visceral pleural invasion VPI in NSCLC patients (test set) | |||
Measure | CT-feature model alone | Radiomics model alone | Radiomics plus CT-feature model |
| AUC | 0.71 | 0.81 | 0.83 |
"The contrast-enhanced CT-based radiomics model demonstrated promising diagnostic performance for preoperative VPI prediction, potentially serving as a valuable tool for treatment planning in early-stage NSCLC," the authors wrote, although they noted that "further prospective multicenter studies are needed to validate these findings."
Access the full study here.





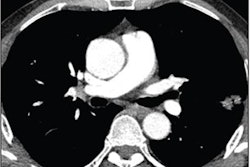



![Images show the pectoralis muscles of a healthy male individual who never smoked (age, 66 years; height, 178 cm; body mass index [BMI, calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared], 28.4; number of cigarette pack-years, 0; forced expiratory volume in 1 second [FEV1], 97.6% predicted; FEV1: forced vital capacity [FVC] ratio, 0.71; pectoralis muscle area [PMA], 59.4 cm2; pectoralis muscle volume [PMV], 764 cm3) and a male individual with a smoking history and chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder (COPD) (age, 66 years; height, 178 cm; BMI, 27.5; number of cigarette pack-years, 43.2, FEV1, 48% predicted; FEV1:FVC, 0.56; PMA, 35 cm2; PMV, 480.8 cm3) from the Canadian Cohort Obstructive Lung Disease (i.e., CanCOLD) study. The CT image is shown in the axial plane. The PMV is automatically extracted using the developed deep learning model and overlayed onto the lungs for visual clarity.](https://img.auntminnie.com/mindful/smg/workspaces/default/uploads/2026/03/genkin.25LqljVF0y.jpg?auto=format%2Ccompress&crop=focalpoint&fit=crop&h=112&q=70&w=112)