Iranian nuclear medicine physicians diagnosed COVID-19 in an asymptomatic patient undergoing technetium-99m (Tc-99m) SPECT/CT imaging for prostate cancer, according to a March 15 report in the Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine.
This is the first such reported case of pulmonary uptake of the radiotracer Tc-99m prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA), the authors wrote.
Dr. Forough Kalantari, an assistant professor of nuclear medicine at the University of Medical Sciences in Tehran, and colleagues, wrote that a 70-year-old asymptomatic patient with biopsy-proven prostate cancer and a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) level of 36 ng/ml underwent Tc-99m PSMA-SPECT/CT imaging for initial treatment planning.
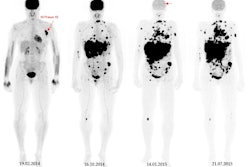
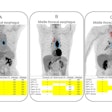
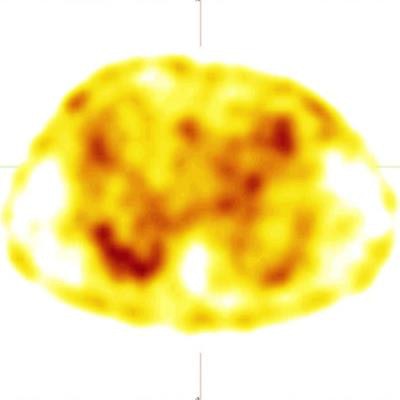
Whole-body images using a hybrid SPECT/CT scanner (Symbia Intevo, Siemens Healthineers) four hours after radiotracer injection showed heterogeneous uptake of Tc-99m PSMA in prostate lobes consistent with previously known malignancy. Yet the researchers also observed an incidental finding: multifocal, bilateral, and peripheral ground-glass opacities in lungs with mild tracer uptake.
"Although the patient had no respiratory symptoms, RT-PCR was performed and the result was positive," Kalantari wrote.
She noted that previous cases of incidental detection of COVID-19-associated pneumonia have been reported in studies using gallium-68 (Ga-68) PSMA-PET/CT, F-18 FDG-PET/CT, and thyroid scintigraphy, but that this is the first case of COVID-19 detected in a patient by Tc-99m PSMA-SPECT/CT imaging.
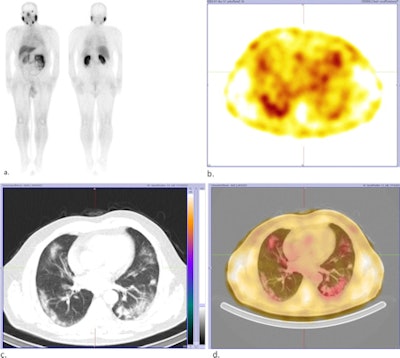 a) Whole-body Tc-99m PSMA study with faint uptake in the chest region as well as physiologic distribution of radiotracer. b) SPECT reveals mild peripheral Tc-99m PSMA uptake in the lung fields. c) CT shows multifocal, bilateral, and peripheral ground-glass opacities in lungs. d) Fused SPECT/CT shows the PSMA uptake is matched by ground-glass opacities in the lung (left lung COVID-related consolidation also shows the same uptake but is not apparent in this cut due to respiratory motion misregistration, the authors noted). Images courtesy of the Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine.
a) Whole-body Tc-99m PSMA study with faint uptake in the chest region as well as physiologic distribution of radiotracer. b) SPECT reveals mild peripheral Tc-99m PSMA uptake in the lung fields. c) CT shows multifocal, bilateral, and peripheral ground-glass opacities in lungs. d) Fused SPECT/CT shows the PSMA uptake is matched by ground-glass opacities in the lung (left lung COVID-related consolidation also shows the same uptake but is not apparent in this cut due to respiratory motion misregistration, the authors noted). Images courtesy of the Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine.The scan was performed as part of a trial ultimately comparing two imaging approaches -- the use of Ga-68 PSMA-PET/CT or Tc-99m SPECT/CT -- for detecting metastatic disease in prostate cancer patients, Kalantari added.
"As many COVID-19 patients are asymptomatic, it is necessary for nuclear medicine departments to review lung window filed in hybrid imaging even in unrelated pathologies," she concluded.