Dear Advanced Visualization Insider,
3D-printing technology has been utilized in radiology for over a decade. But how are 3D-printed models and guides being used clinically today and what benefits do they provide?
Researchers recently analyzed the cases that have been submitted to the RSNA-ACR 3D Printing Registry, which has been up and running for over a year. They shared their findings in a presentation at RSNA 2022 in Chicago.
You can learn all about their report in this edition's Insider Exclusive.
Speaking of 3D printing, the technology could also have an important role to play in producing molybdenum-99 (Mo-99), the precursor to the technetium-99m isotope commonly used in nuclear medicine, according to a group from Poland. Learn more about their patent for increasing production of Mo-99.
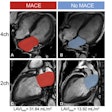
In other advanced visualization news, CT radiomics has revealed significant associations between race and ethnicity and treatment efficacy for metastatic colorectal cancer. These findings suggest that more work is needed to determine how a diverse population responds to treatment of these patients, according to the researchers.
CT radiomics also appears to offer value in classifying subtypes of epithelial ovarian cancer. A research team found that their model could achieve excellent performance for differentiating between high-grade and non-high-grade serous carcinoma.
The Radiology journal's top image of 2022 was a cinematic 3D-rendered image that depicted unusual pathology in a case of a 38-year-old woman with Marfan syndrome who underwent resection for a presumed right ovarian cyst. Check out the award-winning image. Meanwhile, automated body composition analysis may be able to help opportunistically identify sarcopenia on contrast-enhanced abdominopelvic CT exams, according to another study.
Also, 3D virtual reality (VR) simulation-based learning appears to improve the performance of first-year radiography students in clinical settings. The researchers from Ireland concluded that these results bode well for the use of VR in training novice radiographers.
In developments in image-guided surgery, an ultrasound-guided technique was effective enough to eliminate the need for a guide wire in women with ductal carcinoma in situ. And an artificial intelligence model based on x-ray radiomics features could predict mortality risk in COVID-19 patients.
Is there a story you'd like to see covered in the Advanced Visualization Community? Please feel free to drop me a line.
Happy holidays from all of us at AuntMinnie.com!