Dear Advanced Visualization Insider,
Body composition analysis will once again take center stage in this issue of the Advanced Visualization Insider.
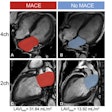
New research published July 25 found that AI-performed body composition analysis of low-dose CT lung cancer screening exams could improve predictions of death from lung cancer, cardiovascular disease, or all causes. What else did they find? Check this edition's Insider Exclusive for all of the details.
Meanwhile, CT-derived body composition biomarkers also show potential for categorizing the level of frailty in older adults, as well as for projecting treatment outcomes in patients undergoing elective intervention for an abdominal aortic aneurysm.
Speaking of predictions, an AI algorithm can improve the prediction of cirrhosis in liver disease patients. What's more, an AI model that incorporates data from an MRI biomarker can help clinicians to forecast response to chemotherapy for breast cancer.
A deep-learning model that combines radiomics analysis of preoperative ultrasound images and biopsy slides can differentiate between luminal and nonluminal breast cancers at early stages, according to a recent study. And ultrasound attenuation imaging can detect hepatic steatosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
An AI model that analyzes CT radiomics features and clinical information can also improve outcome predictions in patients with acute ischemic stroke, while another algorithm could enable opportunistic screening for splenomegaly. CT radiomics features can also be utilized to accurately identify chronic obstructive pulmonary disease as well as to detect in-stent coronary restenosis.
A computational method that incorporates genomic and tau PET imaging data can differentiate the four subtypes of Alzheimer's disease. In addition, multiple myeloma treatment outcome predictions can be bolstered with the help of radiomics models based on F-18 FDG-PET/CT imaging features.
In other advanced visualization developments in molecular imaging, a PET tracer model can quantify cardiac amyloidosis burden. And an augmented PET scanning technique can enhance the resolution and sensitivity of clinical whole-body PET/CT imaging.
Is there a story you'd like to see covered in the Advanced Visualization Community? Please feel free to drop me a line.