J Nucl Med 1994 Jul;35(7):1087-94
Technetium-99m-HMPAO SPECT in partial status epilepticus.
Tatum WO, Alavi A, Stecker MM.
In this paper we correlate the findings on 99mTc-HMPAO brain SPECT with the
results of clinical examinations and electroencephalography to determine the
utility of SPECT in the evaluation of patients with suspected status epilepticus.
METHODS: Thirteen patients with suspected status epilepticus underwent serial
neurologic examinations, serial electroencephalograms, CT/MRI scanning and
99mTc-HMPAO SPECT. Seven patients were diagnosed with status epilepticus and six
patients received other neurological diagnoses. RESULTS: All patients with
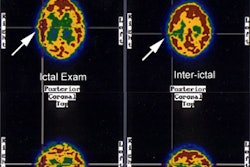
status epilepticus at the time of the brain SPECT scan demonstrated focal
hyperperfusion on SPECT in an area concordant with that suggested by EEG. One
patient with status epilepticus demonstrated a persistent area of hyperperfusion
on SPECT 24 hr after the cessation of status with no evidence of breakdown in
the blood-brain barrier demonstrated by 99mTc-DTPA SPECT. No patient in this
study without a diagnosis of status epilepticus had focal areas of
hyperperfusion on SPECT. CONCLUSION: We suggest that a 99mTc-HMPAO SPECT scan
demonstrating focal hyperperfusion in a patient being evaluated for partial
status epilepticus is nonspecific. Even in the absence of a structural lesion
causing local breakdown in the blood-brain barrier, it may indicate either
ongoing status epilepticus or recently terminated status. However, a SPECT scan
demonstrating no area of focal hyperperfusion argues against the diagnosis of
partial status.