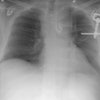
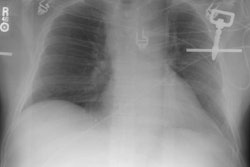
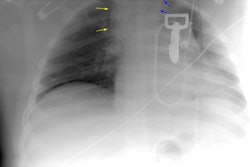
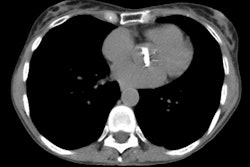
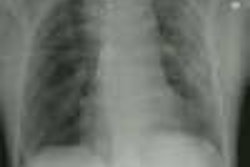
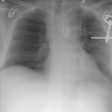
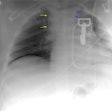
Imaging of acute thoracic aortic injury due to blunt trauma: a review.
Patel NH, Stephens KE Jr, Mirvis SE, Shanmuganathan K, Mann FA
Much recent work on the use of computed tomography (CT) and transesophageal
echocardiography in screening for and facilitating the diagnosis of acute
thoracic aortic injury in the patient with blunt chest trauma has shown
favorable results. This has led some physicians to question whether conventional
thoracic aortography is still the reference standard. The purpose of this
review article is to summarize the epidemiology and pathophysiology of
acute thoracic aortic injury, the current status of the individual imaging
modalities in use, and the surgeon's perspective. Despite a burgeoning
literature and a confouding array of clinical and imaging advances, timely
diagnosis of acute thoracic aortic injury remains a challenge. To overcome
this problem, some trauma centers have used CT, transesophageal echocardiography,
or both, in their diagnostic algorithm for acute thoracic aortic injury.
These diagnostic algorithms are individually tailored by each institution
and are still under investigation; therefore, no definite conclusions can
be reached.