J Nucl Med 1993 Nov;34(11):1892-8
Clinical evaluation of interictal fluorine-18-fluorodeoxyglucose PET in
partial epilepsy.
Henry TR, Engel J Jr, Mazziotta JC.
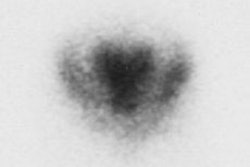
Interictal [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography (PET) is
useful in presurgical evaluation of medically refractory partial epilepsies.
Limited replicability of image interpretation may restrict this application. We
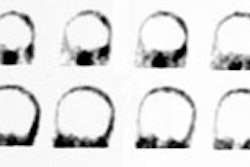
investigated interpretation replicability in 241 18F-FDG studies performed with
three different tomographs in partial epilepsy patients. Two investigators
independently interpreted the studies with a standardized evaluation protocol
and without knowledge of the subjects. Replicability of these unbiased
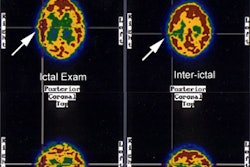
interpretations in detection of regional hypometabolism was best for studies
performed with the highest performance tomograph. Interictal 18F-FDG studies
performed with this tomograph revealed regional hypometabolism in 62% of
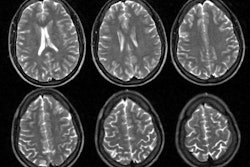
patients who had normal cerebral magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Replicability
of interpretations in detecting regional hypometabolism was adequate for
clinical application of interictal 18F-FDG studies performed with any of the
tomographs.