The Food and Drug Administration, the National Cancer Institute, and the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services this month announced a new initiative to collaborate on improving the development of cancer therapies and the outcomes for cancer patients through biomarker development and evaluation.
Called the Oncology Biomarker Qualification Initiative (OBQI), the program is designed to speed the development and evaluation of cancer therapies via biomarkers, which are biologic indicators of disease or therapeutic effects that can be measured through dynamic imaging tests, as well as tests on blood, tissue, and other biologic samples.
The goal of OBQI is to validate particular biomarkers so that they can be used to evaluate new, promising technologies in a way that will shorten clinical trials, reduce the time and resources spent during the drug development process, improve the linkage between drug approval and drug coverage, and increase the safety and appropriateness of drug choices for cancer patients.
Biomarker research will be focused in four key areas: standardizing and evaluating imaging technologies to see in more detail in how treatments are working; developing scientific bases for diagnostic assays to enable personalized treatments; instituting new trial designs to utilize biomarkers; and pooling data to ensure that key lessons are shared from one to trial to another.
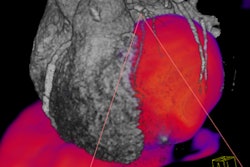
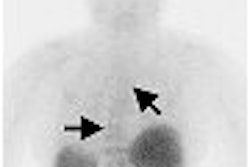
The first OBQI project will attempt to validate and standardize the use of FDG-PET in trials of patients being treated for non-Hodgkin's lymphoma to determine if FDG-PET is a predictor of tumor response.
By AuntMinnie.com staff writers
March 2, 2006
Copyright © 2006 AuntMinnie.com