Radiopharmaceutical developer Navidea Biopharmaceuticals is promoting clinical data from a study comparing the performance characteristics of two agents used for imaging beta-amyloid protein deposits.
The study was presented at the Alzheimer's Association International Conference (AAIC) held last week in Vancouver, British Columbia.
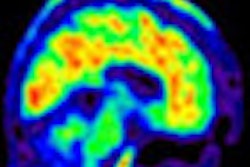
Dr. Christopher Rowe, director of the department of nuclear medicine and center for PET at Austin Health in Melbourne, Australia, presented results from a blinded reader analysis. The analysis examined imaging characteristics of the benchmark amyloid imaging agent carbon-11-labeled Pittsburgh Compound B (PiB) and Navidea's F-18 AZD4694 amyloid imaging candidate.
AZD4694 is intended for use in the imaging and evaluation of patients with signs or symptoms of cognitive impairment such as with Alzheimer's disease. It binds to beta-amyloid deposits in the brain that can be imaged with PET scans.
The two agents were employed to sequentially image the brains of 45 participants, including three patients with frontotemporal dementia, seven patients with probable Alzheimer's disease, 10 patients with mild cognitive impairment, and 25 healthy elderly individuals who were controls.
The analysis evaluated and compared binding kinetics, standardized uptake value ratios (SUVRs) in three time intervals, and nonspecific white-matter retention. The performance of the two types of imaging agents was very similar, according to the company.
Navidea also reported that it received approval on July 13 from the New England Institutional Review Board for its phase II AZD4694 protocol for a trial expected to start within several months.