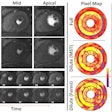
Finnish researchers have developed an imaging technique to reduce the effect of respiratory motion on PET image quality, according to a new study published in Physics in Medicine and Biology.
The study, led by Tuomas Koivumäki from the University of Eastern Finland, details how image reconstruction based on patient breathing patterns can enhance imaging in oncology and cardiac applications (Phys Med Biol, October 7, 2014, Vol. 59:21).
The technique uses bioimpedance, which acquires data needed for motion compensation and can be integrated into electrocardiogram (ECG) measurements to monitor heart function during PET scans.
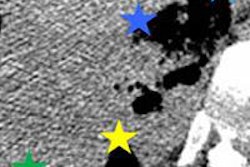
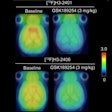
The study first used computational models and test subjects to determine an optimum bioimpedance measurement for the simultaneous calculation of respiratory and cardiac gating signals. The second phase of the study analyzed whether bioimpedance techniques could be used to reduce respiration-related degradation of PET images.
The researchers were able to synchronize images with bioimpedance to create sharper details. Motion compensation also significantly influenced different clinical parameters derived from the images.