Wednesday, December 2 | 11:20 a.m.-11:30 a.m. | SSK02-06 | Room E450A
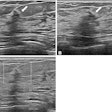
Follow-up ultrasound -- rather than additional axillary imaging -- is just fine for tracking abnormal lymph nodes found on screening breast ultrasound, as long as they do not have an extranodal extension, according to researchers from South Korea.Led by Dr. Jieun Koh of Yonsei University in Seoul, the group evaluated the positive predictive value (PPV) of ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration (FNA) and the cancer detection rate for incidentally detected abnormal axillary lymph nodes in patients who underwent screening ultrasound.
Koh's group reviewed ultrasound-guided FNA results for 72 abnormal lymph nodes found on 50,488 ultrasound screening exams. The exams were conducted between January 2005 and December 2011.
The positive predictive value of ultrasound-guided FNA was 2.8% (two of 72 lymph nodes) and the cancer detection rate was 0.004% (two of 50,488 ultrasound exams).
The findings suggest that PPV and the cancer detection rate are too low to recommend axillary ultrasound during breast ultrasound screening. Koh and colleagues concluded that follow-up ultrasound for these nodes is an acceptable way to track them.