Ultrasound has been used for decades to help humans visualize the inside of the body. Now, it's helping machines do that, too. Scientists have created a robot that uses ultrasound imaging to draw blood from patients with difficult-to-access veins.
The tabletop machine could one day reduce the need for manual ultrasound or other imaging techniques when medical staff can't access crucial veins, according to a research paper published online on February 14 in Nature Machine Intelligence. Early models and tests demonstrated the robot could significantly improve successful vein access and the time to blood drawn.
"Using volunteers, models, and animals, our team showed that the device can accurately pinpoint blood vessels, improving success rates and procedure times compared with expert healthcare professionals," stated senior study author Dr. Martin Yarmush, PhD, a biomedical engineering professor at Rutgers University, in a press release.
How the robot works
Getting timely access to veins is important for many medical procedures. However, about 20% of attempts to draw blood fail, and that percentage is even higher for children, the elderly, and patients who are chronically ill or have experienced trauma.
Because of the problems accessing veins, emergency department staff sometimes use imaging-based assistance, including traditional ultrasound imaging. However, emergency medicine can require quick vein access when radiologists or other trained staff aren't readily available. Therefore, the researchers saw a need for a portable robot that could insert needles and catheters into veins with little human supervision.
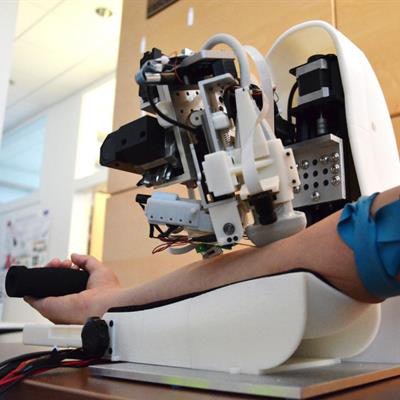
The robot they created first automatically loads a needle and uses near-infrared scanners to obtain and construct a 3D map of the blood vessels. An operator then uses the 3D visualization to identify a target injection site.
Once a site is selected, the robot places an ultrasound transducer above the targeted section. It then uses ultrasound imaging to differentiate arteries from veins, guide the needle into the correct location, and confirm whether cannulation successfully occurred.
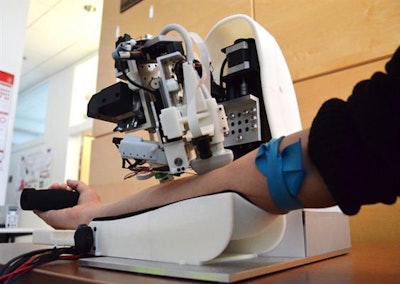 Tabletop robot that uses ultrasound to draw blood. Image courtesy of Dr. Martin Yarmush, PhD, and Alvin Chen, PhD.
Tabletop robot that uses ultrasound to draw blood. Image courtesy of Dr. Martin Yarmush, PhD, and Alvin Chen, PhD.The researchers also added a few fail-safe mechanisms, including instant release upon sudden motion or excess force. Furthermore, the robot automatically loads and disposes of the needle.
Putting the robot to the test
The researchers tested their robot against manual ultrasound-guided vascular access using mathematical models and rodents.
According to the models, the robot-guided machines could result in a whopping 88% success rate on first attempts to draw blood, compared with 68% for traditional ultrasound and 53% for no imaging assistance at all. Furthermore, the robot could significantly reduce the number of failed attempts and time to vein access.
Secondary testing in rodents showed similar results to mathematical modeling. The robot yielded an 87% success rate in rats -- versus 62% for manual ultrasound-guided imaging and 58% for no imaging assistance at all.
It's important to note that while the researchers tested the robot's near-infrared and ultrasound-tracking capabilities with healthy human volunteers, they didn't test the machine's needle insertion properties. As a result, the technology is still a long way off from clinical use.
"The present study demonstrates the preclinical feasibility of autonomous, image-guided robotic vascular access, blood drawing, and fluid delivery," the authors wrote. "The findings provide evidence that by exploiting the capacity of modern deep networks to encode multimodal spatiotemporal imaging information, autonomous systems may be able to outperform human experts on challenging visuomotor tasks in dynamic environments."