Radiology 1997 Nov;205(2):471-8Solitary pulmonary nodules: evaluation of blood flow patterns with dynamic CT.
Zhang M, Kono M
Department of Radiology, Kobe University School of Medicine, Japan.
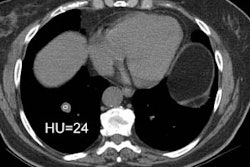
PURPOSE: To evaluate the efficacy of dynamic computed tomography (CT) for differentiating benign from malignant solitary pulmonary nodules (SPNs). MATERIALS AND METHODS: Sixty-five patients with noncalcified SPNs (diameter, < or = 30 mm; 42 malignant, 16 benign, seven inflammatory) underwent single-location dynamic contrast material-enhanced (100 mL, 4 mL/sec) serial CT. Peak height of time-attenuation curves and ratio of peak height of the SPN to that of the aorta were measured. Precontrast attenuation and enhancement pattern were recorded. Perfusion was calculated from the maximum gradient of the time-attenuation curve and the peak height of the aorta. RESULTS: Peak heights of malignant (41.9 HU +/- 2.8) and inflammatory (43.6 HU +/- 7.7) SPNs were significantly higher than that (13.4 HU +/- 2.2) of benign SPNs (P < .001; P < .01). SPN-to-aorta ratios in malignant and inflammatory SPNs were significantly higher than that in benign SPNs (P < .001, P < .05). No statistically significant differences in the peak height and SPN-to-aorta ratio were found between malignant and inflammatory SPNs. Precontrast attenuation of inflammatory SPNs was lower than that of malignant SPNs (P < .05). Perfusion values in malignant and inflammatory SPNs were significantly higher than that of the benign SPNs (P < .01). CONCLUSION: Dynamic CT provides quantitative information about blood flow patterns of SPNs and is an applicable diagnostic method for differentiating SPNs.
Comments:- Comment in: Radiology 1998 Nov;209(2):583; discussion 584-5
- Comment in: Radiology 1998 Nov;209(2):583-4; discussion 584-5
PMID: 9356631, UI: 98019444
General > SPN
Latest in Pulmonary Imaging
General > ChestCT > Images > Air_Trapping
April 2, 2002
General > Biopsy
April 2, 2002