History: A 50-year-old housewife presented with dysphagia and a vague pain in the neck arising from behind the left ear. The patient was experiencing the pain for many years. There were no other complaints.
Findings: General examination was nonconclusive.
Diagnosis: Ossified stylohyoid ligament on the right side with elongated left styloid process.
Differential diagnosis: Nil.
Disease: An elongated styloid process or calcification/ossification of the stylohyoid ligament could be an incidental finding on orthopantomography (OPG), plain film radiography, or CT scan.
Compression on the neurovascular structures in the neck could result in cervicopharyngeal pain. This is described as Eagle's syndrome. The symptoms of Eagle's syndrome are sensation of a foreign body in the throat, dysphagia, and vague facial pain related to an elongated styloid process and a calcified stylohyoid ligament.
The diagnosis of Eagle's syndrome is confirmed by radiographic imaging and by physical examination when an elongated and calcified stylohyoid ligament can be palpated.
Calcification can lead to compression of the adjacent structures that are innervated by the glossopharyngeal and trigeminal nerves and the chorda tympani. There might also be impingement of the plexus of the carotid sheath that produces irritation of the sympathetic nerves.
Radiology:
 |
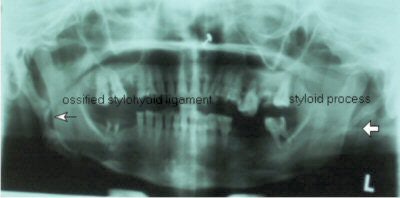 |
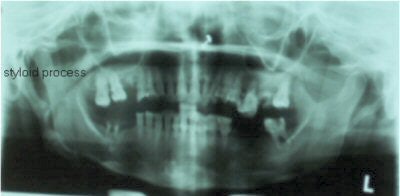
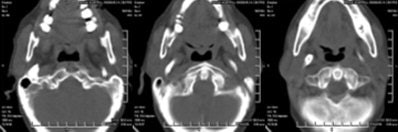
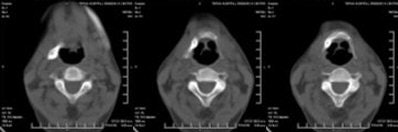
OPG x-ray shows presence of bilateral elongated styloid processes. On the right side, the stylohyoid process is calcified/ossified. Pseudoarticulation of the stylohyoid ligament is seen extending up to the anterior-superior border of the hyoid bone.
 |
 |
 |
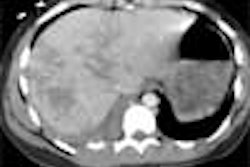
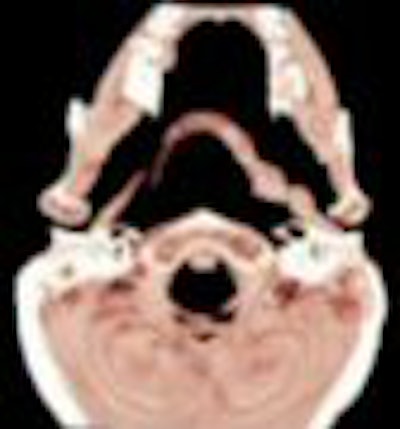
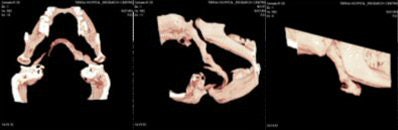
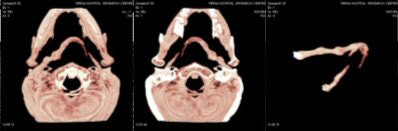
CT scan showed the presence of ossification of the right stylohyoid chain articulating with the hyoid bone. An elongated styloid process was present on the left side.
 |
 |
By Dr Shyam K. Sobti and Dr Madhavan
AuntMinnieIndia.com contributing writers
December 8, 2004
Dr Sobti and Dr Madhavan are lecturers at the Terna Medical College in Mumbai. All images courtesy of Dr Sobti and Dr Madhavan.
Copyright © 2004 AuntMinnie.com