Dear AuntMinnie Member,
The growing effectiveness of artificial intelligence (AI) software in reading mammography and digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) exams has been evident in a number of studies published in recent years. And a new meta-analysis encompassing over 1 million screening breast imaging exams has now concluded that the technology's performance is equal to or better than that of radiologists.
Our article on the research was the most highly viewed on AuntMinnie.com this week. Visit our Women's Imaging Community for the full story.
While you're there, you can also check out other popular stories, including an article on how AI aided radiologists in diagnosing small invasive lobular carcinoma on breast ultrasound images. Speaking of AI and breast ultrasound, another study found that deep learning-based computer-aided diagnosis software could help radiologists to downgrade a significant number of breast lesions, potentially reducing the number of breast biopsies that need to be performed.
Radiation exposure for interventionalists
Although radiation exposure is typically low among interventional radiologists, there can still be a wide range, and more work needs to be done to keep doses as low as possible, a research group from Germany has reported. The team found that doses among doctors performing endovascular stroke treatments were on average 7 µSV per intervention. But in some cases, they reached as high as 64 µSV, according to another of our highly viewed stories this week.
But that wasn't the only article drawing attention this week in our Digital X-Ray Community. A new study found that AI-based analysis of chest radiographs could identify individuals at risk of dying from lung cancer.
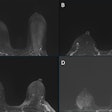
PET shows thermal burns
In a troubling case involving implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs), PET has shown for the first time that multiple shocks from ICDs can result in subcutaneous tissue burns.
Another story from our Molecular Imaging Community that made this week's top 10 list shared how tau PET scans can help diagnose Alzheimer's disease.