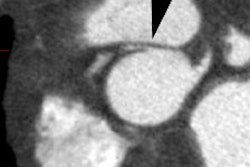
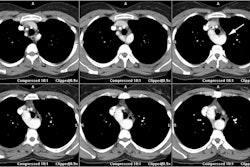
Radiology 2001 Sep;220(3):712-7
ECG-gated reconstructed multi-detector row CT coronary angiography: effect of
varying trigger delay on image quality.
Hong C, Becker CR, Huber A, Schoepf UJ, Ohnesorge B, Knez A, Bruning R, Reiser
MF.
PURPOSE: To evaluate the effectiveness of electrocardiographically (ECG)-gated
retrospective image reconstruction for multi-detector row computed tomographic
(CT) coronary angiography in reducing cardiac motion artifacts and to evaluate
the influence of heart rate on cardiac image quality. MATERIALS AND METHODS:
Sixty-five patients with different heart rates underwent coronary CT angiography.
Raw helical CT data and ECG tracings were combined to retrospectively
reconstruct at the defined consecutive z position with a temporal resolution of
250 msec per section. The starting points of the reconstruction were chosen
between 30% and 80% of the R-R intervals. The relationships between heart rate,
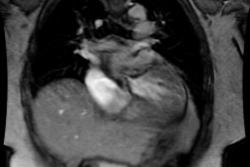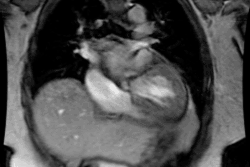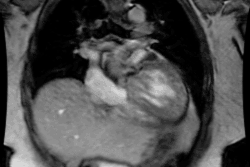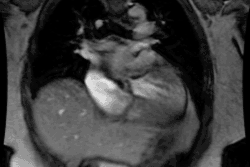
trigger delay, and image quality were analyzed. RESULTS: Optimal image quality
was achieved with a 50% trigger delay for the right coronary artery and 60% for
the left circumflex coronary artery. Optimal image quality for the left anterior
descending coronary artery was equally obtained at 50% and 60% triggering. A
significant negative correlation was observed between heart rate and image
quality (P <.05). The best image quality was achieved when the heart rate was
less than 74.5 beats per minute. CONCLUSION: To achieve high image quality, the
heart rate should be sufficiently slow. Selection of appropriate trigger delays
and a decreasing heart rate are effective to reduce cardiac motion artifacts.