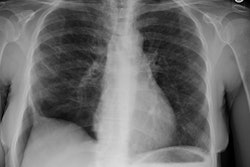
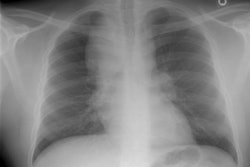
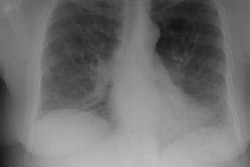
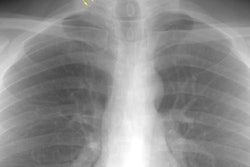
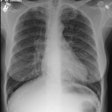
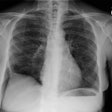
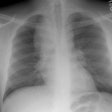
Lung transplantation for lymphangioleiomyomatosis: role of imaging in the assessment of complications related to the underlying disease.
Collins J, Muller NL, Kazerooni EA, McAdams HP, Leung AN, Love RB
PURPOSE: To identify the complications and imaging findings related to lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM) after lung transplantation. MATERIALS AND METHODS: The authors retrospectively reviewed the clinical histories and imaging studies of 13 patients from five major medical centers who underwent unilateral (n = 8) or bilateral (n = 5) lung transplantation for LAM between 1991 and 1997. Complications related to LAM, both before and after transplantation, were recorded. RESULTS: The following LAM-related complications were found during and after transplantation: excessive pleural adhesions (n = 4), native lung pneumothorax (n = 3), chylous effusion (n = 1), chylous ascites (n = 3), complications from renal angiomyolipomas (n = 4), and recurrent LAM (n = 1). Diagnosis could be made or suggested with computed tomography (CT) in all cases. Four patients (31%) died; one patient died of complications of LAM. CONCLUSIONS: Patients who have undergone lung transplantation for LAM have increased morbidity and mortality due to complications related to their underlying disease. These LAM-related complications can be diagnosed or suggested with CT.
PMID: 10207410, UI: 99223817