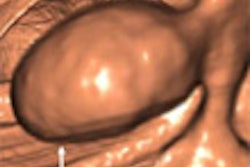
AGRA - Imaging provides a reliable method to localise and characterise lesions in the brachial plexus and differentiate between a mass and other causes of plexopathy. That's according to a presentation at the Indian Radiological and Imaging Association (IRIA) conference, which began today.
Brachial plexus imaging was the subject of a presentation at the opening session of the 58th annual congress of the Indian Radiological and Imaging Association (IRIA) at Agra on Saturday. The talk concluded that MR and US were the key imaging modalities for the disorder.
"MR is the imaging modality of choice for demonstration of brachial plexus lesions. US should be performed as part of preoperative evaluation in post ganglionic brachial plexus pathology," said Dr N. Chidambaranathan, head of the department of radiology and imaging sciences at Apollo Hospitals.
Brachial plexopathy can be of two types: traumatic, which is more predominant, and non-traumatic. In traumatic brachial plexopathy, the treatment approach varies depending on whether it is intraforaminal or extraforaminal. About 25% of brachial plexus injuries are extra-foraminal, according to Chidambaranathan.
High-resolution US can show disruption of nerve continuity with swelling of proximal and distal stump and the wavy course of retracted distal segment, and hypoechoic irregular soft tissue. Segmental fusiform thickening of trunk is also demonstrated.
CT can demonstrate the central portion of the brachial plexus at neural formina and soft-tissue haematoma in the supra clavicular and infra-clavicular region. However, it is limited by poor soft-tissue contrast and beam-hardening artifacts.
The drawback of electromyography (EMG), which measures muscle response to nervous stimulation, is that it cannot distinguish between a mass and other causes of plexopathy. "EMG can be incomplete and misleading," Chidambaranathan said.
MR, on the other hand, can identify spinal-cord injury, the integrity of the nerve root, the location and type of injury, mechanical compression, and associated injury to vessels and bone. It is performed using a phased-array coil or surface coil. A saturation band is used to minimise artifacts.
By N. Shivapriya
AuntMinnieIndia.com staff writer
January 22, 2005
Copyright © 2005 AuntMinnie.com