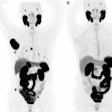
Carbon-11 Pittsburgh compound B (C-11 PiB) PET/CT demonstrates robust capability for detecting cardiac amyloidosis and accurately differentiating its subtypes, according to research presented December 4 at RSNA.
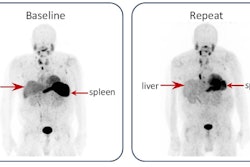
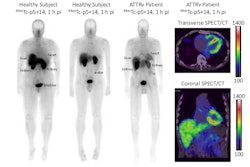
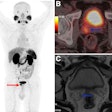
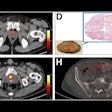
Takashi Norikane, MD, PhD, of Kagawa University in Kagawa, Japan, presented a study in which 81 patients underwent 30-minute PiB-PET/CT scans, with images in patients with the disease clearly indicating light chain amyloidosis (AL amyloidosis) from transthyretin amyloidosis (ATTR amyloidosis).
“Accurate subtype diagnosis is essential in clinical practice,” Norikane told attendees.
Cardiac amyloidosis develops when, for reasons that remain unclear, amyloid proteins misfold and build up in the myocardium. This restricts cardiac function and can lead to heart failure and death. The disease’s subtypes are distinct, as they are caused by different proteins, Norikane explained. Thus, they require different treatment strategies.
While various imaging modalities, including echocardiography, cardiac MRI, and technetium-99m pyrophosphate scintigraphy, are widely used and valuable for diagnosing the disease, they are limited in detecting subtypes, Norikane added. Recently, amyloid PET/CT with C-11 PiB radiotracer has gained recognition for its potential to detect both types, and in this study, Norikane and colleagues further evaluated its ability to differentiate between them.
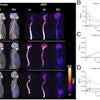
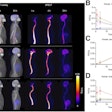
A total of 81 patients underwent dynamic PET/CT scans over 30 minutes after an intravenous bolus injection of C-11 PiB. From the data, the researchers reconstructed both retention index (RI) images showing how much the tracer stayed in the heart over time and standardized uptake value (SUV) images at 10 minutes (SUV010), 20 minutes (SUV1020), and 30 minutes (SUV2030). Finally, to compare uptake between patients, the group used a quantitative metric called the myocardial-to-blood pool ratio (MBR).
According to the analysis, 60 patients were diagnosed with cardiac amyloidosis, eight with the AL subtype and 52 with the ATTR subtype. Across all images, AL cases exhibited significantly higher MBR values compared with both ATTR and nonamyloidosis cases. ATTR cases also demonstrated significantly higher myocardial uptake than nonamyloidosis cases on RI, SUV010, and SUV1020 images.
In addition, a receiver operating characteristic analysis showed that the SUV2030 images yielded the highest diagnostic accuracy for differentiating cardiac amyloidosis from nonamyloidosis (area under the curve [AUC] = 0.960; sensitivity, 93.3%; specificity, 95.2%), while the SUV10 images provided the best performance for distinguishing AL cases from ATTR cases (AUC = 0.851; sensitivity, 87.5%; specificity, 73.5%).
“SUV2030 images optimized amyloidosis detection, while SUV010 images maximized subtype discrimination,” Norikane said.
PiB-PET/CT shows strong promise as a next-generation diagnostic tool for cardiac amyloidosis and offers a potential adjunct to current diagnostic strategies, he concluded.