Artificial intelligence (AI) firm Elucid is highlighting a new study published in Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology on the use of its software to provide phenotyping of atherosclerosis on CT angiography (CTA) exams.
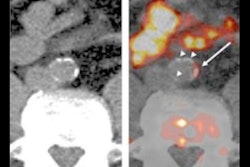
Elucid's software has been trained to estimate plaque morphology and transcriptomes based only on analysis of CTA studies, according to the firm. In the study, which was published online March 11, researchers from Elucid and partner Karolinska Institute in Sweden detailed how supervised models were able to predict 414 coding and noncoding RNAs based on plaque morphology on CTA. They also showed in four patients how models could predict gene expression.
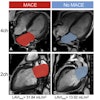
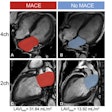
"The results of this pilot study show that atherosclerotic plaque phenotyping by image analysis of conventional computed-tomography angiography can elucidate the molecular signature of atherosclerotic lesions in a multiscale setting," the authors wrote. "The study holds promise for optimized personalized therapy in the prevention of myocardial infarction and ischemic stroke, which warrants further investigations in larger cohorts."