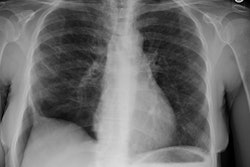
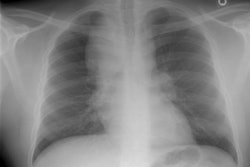
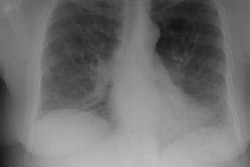
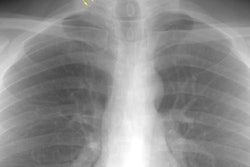
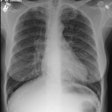
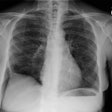
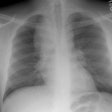
The spectrum of eosinophilic lung disease: radiologic findings.
Kim Y, Lee KS, Choi DC, Primack SL, Im JG
PURPOSE: Eosinophilic lung disease includes various disease entities. Each disease manifests different radiologic findings. The purpose of this review is to present the radiologic findings of the spectrum of eosinophilic lung disease. METHOD: We reviewed the radiologic, histologic, and clinical findings of the spectrum of eosinophilic lung disease from the previous reports and our experiences. RESULTS: Simple pulmonary eosinophilia is characterized by transient and migrating opacities on chest radiography. Acute eosinophilic pneumonia is characterized by acute clinical symptoms and signs and rapid changes of radiographic diffuse reticular lesions. Chronic eosinophilic pneumonia, with more prolonged symptom duration, history of asthma, occurrence of relapse, and radiologic features of subpleural consolidation, can be differentiated from acute eosinophilic pneumonia. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis presents with bilateral central bronchiectasis with or without mucoid impaction. Although these diseases show specific radiographic findings, some show overlapping radiographic features. High-resolution CT enables characterization of parenchymal lesions further by showing internal and marginal features and the exact extent of the lesions. Extrapulmonary organs are involved in Churg-Strauss syndrome and idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome. Asthma is associated with Churg-Strauss syndrome, allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis, chronic eosinophilic pneumonia, and bronchocentric granulomatosis. CONCLUSION: Integration of clinical, laboratory, and radiologic findings enables initial and differential diagnoses of various eosinophilic lung diseases.