Loeffler endocarditis (Hypereosinophilic syndrome)
Clinical:
A rare, eosinophil-mediated injury to the subendocardium resulting in necrosis, thrombosis, and late-stage fibrosis involving both the right and left ventricles [1]. Clinically patients present with CHF, restrictive cardiomyopathy, and thromboembolic events [1]. Lab analysis will demonstrate peripheral eosinophilia with no identifiable etiology [1].
X-ray:
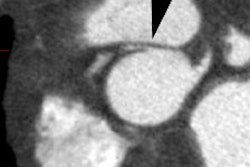
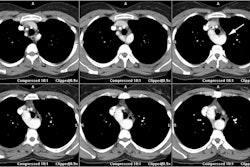
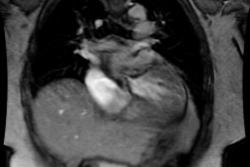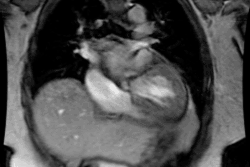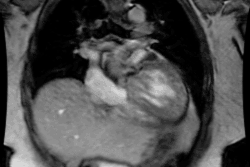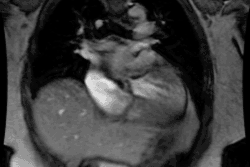
On delayed contrast MR imaging there is intense enhancement of the subendocardial surface that is not limited to a vascular territory (due to cell death and fibrosis) [1]. Apical thrombi can form due to endomyocardial surface damage and stasis [1]. Unlike thrombus asspciated with apical aneurysms and prior infarct, there is no myocardial thinning and no transmural enhancement [1].
REFERENCES:
(1) Radiographics 2009; Cummings KW, et al. A pattern-based approach to assessment of delayed enhancement in nonischemic cardiomyopathy at MR imaging. 29: 89-103