Pneumoconioses:
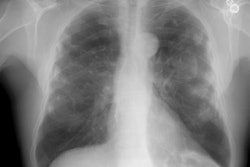
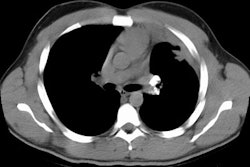
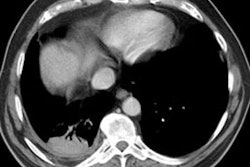
Pneumoconioses are diseases produced by the inhalation of non-living particulate matter (i.e.: dusts). Pneumoconioses can be considered to be fibrogenic (in which the dust is capable of producing a tissue reaction) or non-fibrotic (benign) [1]. Silicosis, coal workers pneumoconiosis, asbestosis, berylliosis, and talcosis are examples of fibrotic pneumoconioses [1]. Siderosis (iron oxide), stannosis (tin oxide), and baritosis (barium sulfate) are non-fibrotic pneumoconises [1].
REFERENCES:
(1) Radiographics 2006; Chong S, et al. Pneumoconiosis: comparison of imaging and pathologic findings. 26: 59-77