Giant Cell Interstitial Pneumonia:
Clinical:
Giant cell interstitial pneumonia (GIP) is a rare form of pulmonary fibrosis caused by exposure to metal compounds such as cobalt or tungsten carbide [1]. GIP is considered a pneumoconiosis [1]. In the condition, the interstitium and alveolar walls are thickened by mononuclear cells, and the diagnostic feature of GIP is the presence of a large number of giant cells filling the air spaces [1].
X-ray:
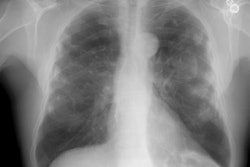
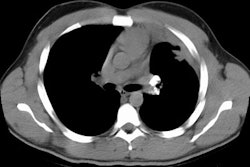
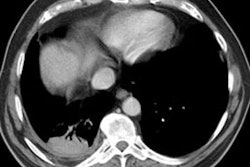
Findings on HRCT include ground-glass opacities, reticular/irregular linear densities, and enlarged mediastinal lymph nodes [1]. Honeycombing can also be seen [1].
REFERENCES:
(1) AJR 2005; Choi JW, et al. Giant cell interstitial pneumonia: high-resolution CT and pathologic findings in four adult patients. 184: 268-272