Common Findings/Artifacts in Tc-MDP Bone Scans:
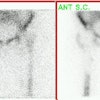
Gastric or thyroid activity:
Due to free pertechnetate if TcMDP is given more than 4-5 hours following its preparation.
Glove phenomenon:
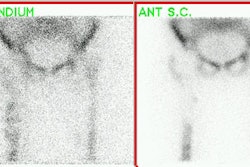
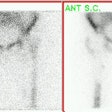
Significant activity in limb distal to injection site due to an arterial injection.
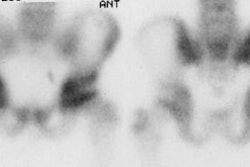
Diffusely increased renal parenchymal activity:
- Poor hydration with delayed excretion of the tracer.
- Nephrocalcinosis: Medullary sponge kidney, Hyperparathyroidism, Renal tubular acidosis and other causes of hypercalcemia.
- Iron overload: Multiple transfusions or hemochromatosis
- Sickle cell: The prominent renal uptake is felt to be related to abnormalities in renal concentrating ability due to medullary ischemia. The kidneys also frequently appear large. Look for associated splenic uptake in a small, calcified spleen.
- Acute Tubular Necrosis (Early Stages)
- Glomerulonephritis
- Drugs: Renal accumulation in this setting is probably the result of interstitial nephritis.
- Chemotherapy: Vincristine, cyclophosphamide, & doxorubicin
- Aminoglycosides
- Amphotericin
Hepatic Uptake:
- Artifact: Recent Tc-Sulfur Colloid study
- Mets (typically focal activity, but can be diffuse if associated with infiltrative mets)
- Hepatic necrosis (diffuse)
- Elevated Al+3 in Tc-99m eluate: Aluminum ion breakthrough can result in the formation of an aluminum-technetium colloid particle. This aluminum effect has also been observed in patients taking aluminum containing antacids- presumably due to in vivo colloid formation.
- Excess colloid technetium oxides (reduced tech [Tc02]): Can occur when the pH of the reaction mixture is alkaline, rather than acidic, or if excess stannous ion is present.
- ?Infiltrating diseases (i.e.: Amyloidosis)
Splenic Uptake:
- Sickle cell disease with small calcified spleen
- Hemosiderosis
- Hodgkin's lymphoma
- Mets
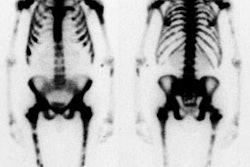
Superscan:
- Diffuse bony mets
- Delayed imaging
- Paget's
- Metabolic:
- Osteomalacia: May see focal sites of increased activity which represent Looser zones
- Renal osteodystrophy/Secondary hyperparathyroidism
- Primary hyperparathyroidism: Focal sites of increased tracer activity are associated with Brown tumors
- Hyperthyroidism
- Acromegaly: Look for prognathism and early degenerative changes characteristic of the disorder.
- Hypervitaminosis D
- Mastocytosis
False Negative Scans or Cold (photon deficient) Lesions:
A. Interruption of local blood flow (infarction):
- Trauma
- Sickle cell crisis
- Bone Infarction
- Aseptic necrosis
- Prior XRT: Typically involves multiple adjacent bones and requires a dose over 4000-5000 rads
B. Predominant osteoclastic activity or primarily bone marrow involvement:
- Highly anaplastic tumors:
- Multiple myeloma
- Neuroblastoma
- Renal Cell Carcinoma
- Thyroid Carcinoma
- Reticulum cell sarcoma (Lymphoma)
- Histiocytosis
- Early Osteomyelitis
C. Overlying attenuation artifact
D. Diphosphonate [Etidronate disodium (EHDP)] therapy [1]:
Etidronate disodium is used in the emergency treatment of hypercalcemia, Paget's disease, and heterotopic ossification. The agent competes with MDP at the skeletal binding sites and can result in almost non-visualization of the skeleton on bone scan. Not all diphosphonate agents are associated with decreased Tc-MDP accumulation [1].
REFERENCES:
(1) J Nucl Med 2001; Carrasquillo JA, et al. Alendronate does not interfere with 99mTc-methylene diphosphonate bone scanning. 42: 1359-1363