Hughes-Stovins Syndrome:
Clinical:
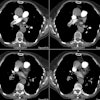
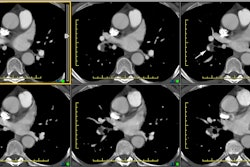
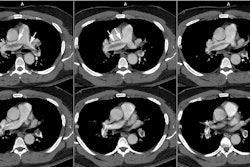
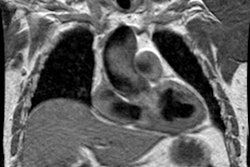
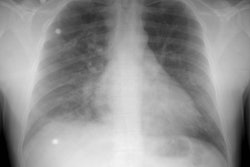
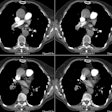
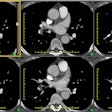
Hughes-Stovin syndrome is an exceedingly rare large vessel vasculitis which usually affects young men (2nd-4th decade) characterized by multiple pulmonary artery aneurysms and venous thrombosis (including dural sinus thrombosis and peripheral thrombophlebitis). The disorder affects pulmonary and frequently bronchial arteries and large systemic veins [5]. Patients present with cough, hemoptysis, dyspnea, intermittent fever, headache, and papilledema. The most frequent cause of death is rupture of an aneuryms into the pulmonary airways. Differential considerations include Behcets syndrome, polyarteritis nodosa, and collagen vascular disorders.REFERENCES:
(1) AJR 1991; Ammann ME, et al. Radiologic findings in the diagnosis of Hughes-Stovin syndrome. 157: 1353-54 (No abstract available)
(2) AJR 1996; Mahlo HR, et al. New approach in the diagnosis of and therapy for Hughes-Stovin syndrome. 167: 817-18 (No abstract available)
(3) AJR 2005; Marten K, et al. Pattern-based differential diagnosis in pulmonary vasculitis using volumetric CT. 184: 720-733
(4) AJR 2005; Ketchum ES, et al. CT angiography of pulmonary artery aneurysms in Hughes-Stovins syndrome. 185: 330-332
(5) Radiology 2010; Chung MO, et al. Imaging of pulmonary vasculitis. 255: 322-341