AJR Am J Roentgenol 1995 Nov;165(5):1131-1138. Diagnosis of central pulmonary embolism with helical CT: role of two-dimensional multiplanar reformations.
Remy-Jardin M, Remy J, Cauvain O, Petyt L, Wannebroucq J, Beregi JP
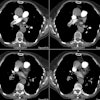
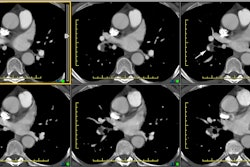
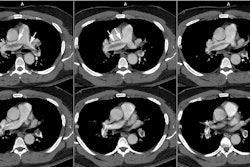
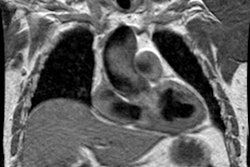
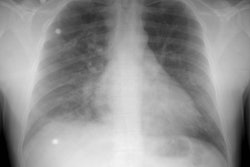
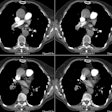
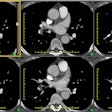
OBJECTIVE. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the role of multiplanar two-dimensional (2D) reformations in the diagnosis of central pulmonary embolism with helical CT. SUBJECTS AND METHODS. Thirty-five patients with suspected pulmonary embolism underwent contrast-enhanced helical CT of the pulmonary arterial tree. Two sets of images were analyzed: overlapped transverse sections and 2D reformatted images of 10 obliquely oriented arteries (intralobar pulmonary artery, A2, A4+5, A6, and A10 [A = artery]) selected on three-dimensional shaded surface displays of each pulmonary arterial tree. RESULTS. Among the 20 patients with unequivocal central pulmonary emboli on transverse sections (group 1), 2D reformations enabled a more precise analysis of the extent of thromboembolic disease in 13 cases. These patients underwent no further diagnostic procedure. In six patients (group 2), transverse sections alone excluded central pulmonary embolism with angiographic (n = 2) or scintigraphic (n = 4) confirmation. No additional information was provided with the 2D reformations. In nine patients with an uncertain diagnosis of pulmonary embolism on transverse sections (group 3), 2D reformations enabled us to exclude central emboli in all the cases, with angiographic (n = 4) or scintigraphic (n = 5) confirmation. In groups 1 and 3, 2D reformations provided adequate visualization of obliquely oriented arteries (n = 30) and enabled assessment (n = 2) or exclusion (n = 28) of endovascular changes, a clear distinction between endoluminal and perivascular abnormalities (n = 7), or a precise evaluation of extensive mural thrombi (n = 6). CONCLUSION. Our results show that 2D reformations enable confident exclusion of pulmonary embolism on inconclusive helical CT examinations and improve analysis of the extent of thromboembolic disease.
PMID: 7572490, MUID: 96021942