J Thorac Imaging 1996;11(3):187-197. Rounded atelectasis.
Batra P, Brown K, Hayashi K, Mori M
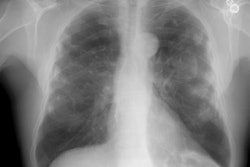
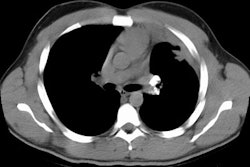
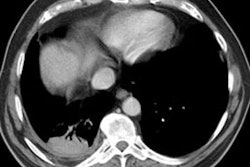
Rounded atelectasis (RA) is a special type of peripheral lung collapse that develops as a result of pleural disease. Most cases have been attributed to asbestos inhalation, but many other causes have also been implicated. It is usually detected incidentally in an asymptomatic older man. RA can be diagnosed by a constellation of radiologic findings. It appears as a rounded masslike opacity in the peripheral lung adjacent to thickened pleura and with curvilinear opacities of bronchi and vessels (comet tail) extending from the site of RA toward the hilum. Volume loss of the affected lobe is uniformly present. In addition to the classic lesion, a spectrum of atypical lesions has also been described. Computed tomography (CT) and high-resolution CT demonstrate the full extent of disease better than chest radiography. Familiarity with this benign condition is important to differentiate it from other pulmonary and pleural diseases and to prevent unnecessary invasive procedures and surgical resection.
PMID: 8784732, MUID: 96379169