Radiology 2001 Dec;221(3):606-13
Multi-Detector Row Spiral CT Pulmonary Angiography: Comparison with
Single-Detector Row Spiral CT.
Raptopoulos V, Boiselle PM..
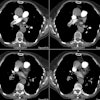
PURPOSE: To compare vascular conspicuity and ability to connect pulmonary
arterial branches on pulmonary angiograms obtained with helical multi-detector
row computed tomography (CT) with those on pulmonary angiograms obtained with
helical single-detector row CT. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Of 93 consecutive
patients suspected of having pulmonary embolism, 48 underwent scanning with
multi-detector row CT and 45 with single-detector row CT; scans were obtained in
9 seconds and 28 seconds with 2.5-mm and 3.0-mm collimation, respectively. The
lungs were divided into three zones: central, middle, and peripheral. Two
independent observers used five-point grading scales. RESULTS: Conspicuity of
pulmonary arteries in the central zone was ranked equal (median of 5), but in
the middle and peripheral zones it was significantly higher at multi-detector
row CT than at single-detector row CT (median 5 vs 4 and 4 vs 3, P <.001,
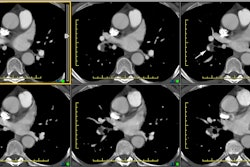
respectively). In addition, multi-detector row CT improved the ability to
connect peripheral arteries with their more centrally located pulmonary artery
of origin in the peripheral but not the middle zone on transverse images and in
both zones on multiplanar images. Viewing with a modified window setting (width,
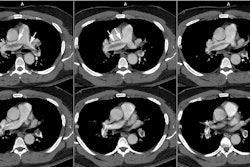
1,000 HU; level, -100 HU) significantly increased pulmonary arterial
conspicuity. Contrast material column in the pulmonary arteries was
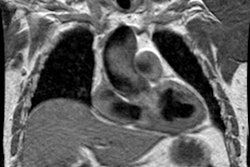
significantly more homogeneous at multi-detector row CT. CONCLUSION: Use of
multi-detector row CT significantly improves pulmonary arterial visualization in
the middle and peripheral lung zones.