J Nucl Med 1997 Mar;38(3):366-8
Impact of lymphoscintigraphy on sentinel node identification with
technetium-99m-colloidal albumin in breast cancer.
Pijpers R, Meijer S, Hoekstra OS, Collet GJ, Comans EF, Boom RP, van Diest PJ,
Teule GJ.
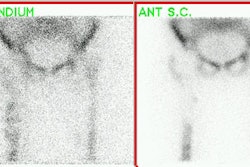
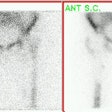
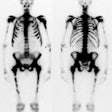
Identification of the sentinel node by using colloidal tracers and a gamma probe
or lymphoscintigraphy could be an effective alternative for the complicated
original dye-oriented approach. We studied the sentinel node detection rate
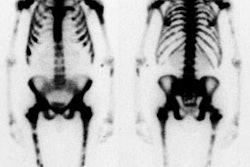
using early and delayed imaging in breast cancer patients. METHODS: Thirty-seven
patients were imaged 2 hr and 18 hr after peritumoral injection of
99mTc-colloidal albumin. Preoperatively, axillary foci were located with a
handheld gamma probe that was also used to isolate radiolabeled nodes from the
axillary dissection specimens. The predictive value of the sentinel node for the
axillary tumorstatus was evaluated with histological examination. RESULTS: Two
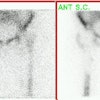
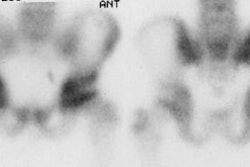
and 18 hr after injection, lymphoscintigraphy revealed one to three separate
axillary lymph nodes in 33 and 34 patients, respectively. In 30 patients the
axillary foci were easily localized with the gamma probe preoperatively. In all
34 patients (92%), with visualized axillary foci, at least one radioactive
sample could be retrieved using the gamma probe (total 53 samples). Metastases
were found in the sentinel nodes of 11 patients, in seven of 11 being the only
tumor-positive lymph node in the axilla. There were no false-negative sentinel
nodes. CONCLUSION: The selective targeting and prolonged intranodal retention of
99mTc-colloidal albumin allows successful sentinel node identification in most
(92%) patients.