Monday, December 1 | 3:30 p.m.-3:40 p.m. | SSE19-04 | Room S505AB
In this study, researchers are touting the prowess of PET imaging with carbon-11-labeled Pittsburgh Compound B (C-11 PiB) for evaluating and differentiating Alzheimer's disease and poststroke dementia.Lead author Sirong Chen, PhD, a research fellow in medical imaging at Hong Kong Sanatorium and Hospital, said that clinical assessment of concurrent Alzheimer's in poststroke dementia is difficult, as typical Alzheimer's features can also be found in vascular dementia.
"Concurrent Alzheimer's is common in poststroke dementia and may warrant specific treatments targeting amyloid plaque in these patients, in addition to prevention of recurrent stroke," he wrote in an email to AuntMinnie.com.
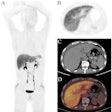
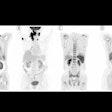
The study included 39 poststroke dementia patients (mean age, 77 years), 39 age- and sex-matched individuals who were in the early stages of Alzheimer's (mean age, 76 years), and 39 healthy controls (mean age, 72 years). All subjects underwent PET/CT at five minutes and 35 minutes after C-11 PiB injection.
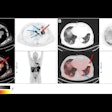
The researchers analyzed several regions of the brain associated with dementia and stroke, including the frontal gyrus, gyrus rectus, superior parietal lobe, posterior cingulate, precuneus, lateral temporal lobe, occipital lobe, caudate, and putamen.
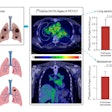
Using a combination of global PIB binding (GPB) data from those brain regions normalized to the cerebellum, receiver operator characteristics (ROC) analysis for the Alzheimer's patients and normal subjects, and a visual evaluation of increased PiB uptake in the poststroke dementia patients, the researchers determined a GPB cutoff point for an Alzheimer's diagnosis.
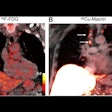
With a GPB cutoff value of 1.42, a visual evaluation of PiB uptake identified 14 (36%) poststroke dementia patients who also had Alzheimer's. As one might expect, poststroke dementia patients with concurrent Alzheimer's had significantly greater GPB results than the normal controls.
"C-11 PiB PET had a high distinguishing power for concurrent Alzheimer's in poststroke dementia from pure vascular dementia by the detection of PiB binding in brain areas known to accumulate high beta-amyloid plaques in early Alzheimer's," Chen added.
Chen and colleagues plan to continue their research in a cohort of poststroke patients with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) to see whether C-11 PIB PET has a high predictive value for Alzheimer's based on long-term follow-up.
"We would compare the C-11 PiB distribution pattern of this cohort of MCI patients with that of the poststroke dementia patients with concurrent Alzheimer's," he said.