SALT LAKE CITY - Both ultrasound and MRI hit the mark for detecting a contusion in a female ice hockey player whose scrimmage practice with male players got a little rough at this week’s Olympic Winter Games.
Dr. Julia Crim, chief of musculoskeletal imaging for the Olympic Polyclinic, did the ultrasound exam herself and said it was a unique experience.
"I have never in my life done an ultrasound on anybody with a quadriceps anywhere near this size," she explained. "I put down the transducer and I thought "Well, this is all normal muscle, what in the world is deep to it?’ I realized that in an ordinary individual, it would be the depth of the entire quadricep. In this individual, it was just her superficial muscle with the huge vastus intermedius down below it."
Sonography was performed with the clinic’s HDI 5000 SonoCT scanner (Philips Medical Systems, Bothell, WA) using a panoramic field of view. The vastus lateralis showed normal echogenicity throughout. The muscle under it, the vastus intermedius, was heterogeneous in echogenicity and was consistent with edema.
"So you have a beautiful, perfectly normal vastus lateralus, and then deep to it, we have a diffusely abnormal vastus intermedius. It’s got a lot of abnormal signal within it, but it’s not completely torn. You can say it’s all extensive interstitial tearing," Crim said.
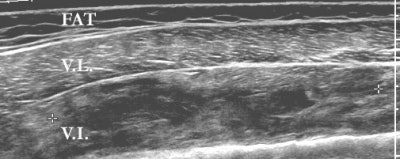 |
| Coronal ultrasound image of the lateral thigh. Image was obtained using a panoramic field of view. The superficial muscle, the vastus lateralis (VL), shows normal echogenicity throughout. The muscle deep to it, the vastus intermedius (VI), is heterogeneous in echogenicity, consistent with edema. Markers delimit a 16-cm-long region with multiple fluid collections which represents more focal hematoma. |
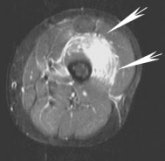 |
| Same patient, axial MRI, FSE T2FS. Arrows point to the hematoma in the vastus intermedius. |
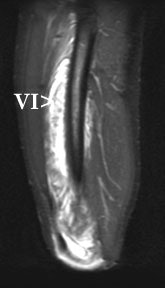 |
| Same patient, sagittal MRI, FSEIR. Arrows point to the vastus intermedius. Just as on the ultrasound, focal fluid collections surrounded by diffuse muscle edema are visible. |
The protocol for the MR scan included images in the axial plane, T2-weighting, fast spin echo (FSE), and fat saturation. As with the ultrasound, focal fluid collections were surrounded by diffuse muscle edema.
"There’s perfect agreement between the ultrasound and the MR," Crim said. "This patient was treated with aggressive physical therapy." While the patient has yet to undergo a follow-up MR, she did play in the women’s ice hockey preliminary game on Tuesday.
By Shalmali Pal
AuntMinnie.com staff writer
February 14, 2002
Copyright © 2002 AuntMinnie.com