A new study has found similarities between the performance of digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) combined with synthesized mammography and the performance of DBT plus full-field digital mammography (FFDM). But the two combinations differed in how they handled the recall of patients with calcifications.
There were no statistically significant differences between DBT plus synthesized mammography and DBT plus FFDM for recall rate, cancer detection rate, and positive predictive value when used for breast screening, according to research published September 15 in Academic Radiology.
But while they had similar recall rates, the modality combinations actually recommended recalling different patients, particularly ones with breast calcifications, according to a team led by Dr. Monica Huang from the University of Texas.
Synthesized mammograms derived from DBT data were developed to give radiologists the additional views of the breast found on FFDM studies without the radiation dose of an additional exam. Previous research has shown that interpretation of DBT images obtained along with FFDM resulted in a reduction in recall rates and an increase in cancer detection. This has allowed DBT to gain in popularity when used in conjunction with synthesized or full-field digital mammography in screening patients, the researchers said.
However, few studies have examined the types of imaging findings prompting recall or go into detail on recall differences and disagreements between these combined methods.
"Although a number of retrospective studies have compared the recall rate and cancer detection ... few prospective studies have compared the clinical performance of these different breast imaging modalities," Huang and colleagues wrote.
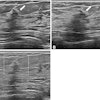
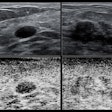
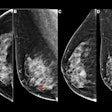
The team wanted to prospectively compare the performance of synthesized mammography plus DBT and FFDM plus DBT in terms of recall rate, cancer detection rate, and positive predictive value, as well as the imaging findings that might prompt a patient to be recalled. Imaging findings included the following: asymmetry, focal asymmetry, mass, architectural distortion, and calcifications. Data was collected from 1,022 women between December 2015 and January 2017.
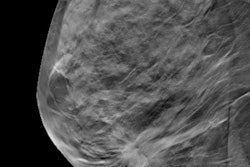
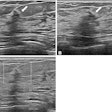
The researchers found that FFDM plus DBT detected eight cancers, while synthesized mammography plus DBT detected seven. The latter method missed one cancer with calcifications.
| FFDM + DBT vs. synthesized mammography + DBT | ||
| FFDM + DBT | Synthesized mammography + DBT | |
| Recall rate | 7.9% | 7.3% |
| Cancer detection rate (per 1,000) | 7.8 | 6.8 |
| Positive predictive value | 9.9% | 9.3% |
Both methods also showed similar performance when finding calcifications, with synthesized mammography plus DBT finding 26 calcifications, while full-field digital mammography plus DBT found 27. Despite this, the modalities disagreed on patient recall for additional imaging in 19 patients, with 13 being recalled for calcifications.
Synthesized mammography plus DBT recalled six patients that full-field digital mammography plus DBT did not recall. Meanwhile, full-field digital mammography plus DBT recalled seven patients that synthesized mammography plus DBT did not recall.
"Although the clinical significance of this difference in appearance of calcifications is yet unproven, it is important to keep this in mind when evaluating different types of DBT acquisition equipment and synthesized mammography reconstruction software," Huang and colleagues wrote.
The study authors touted their study as being unique in comparing interpretations for both methods in the same patient by the same radiologist, with imaging of both types of mammography at the same time point. They said this eliminated variances in radiologist performance, population, and imaging quality.
The researchers wrote that future studies need larger sample sizes to assess the potential clinical significance of their reported recall and cancer detection differences. They also said future studies should compare and contrast different types of DBT image acquisition and synthesized mammography reconstruction software.
"With time, improving technology will result in the continued improvement of synthesized mammography and DBT image quality, which may surpass current full-field digital mammography plus DBT in terms of diagnostic abilities," they said.