From the archives of the AFIP: pulmonary vasculature: hypertension and infarction.
Frazier AA, Galvin JR, Franks TJ, Rosado-De-Christenson ML
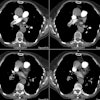
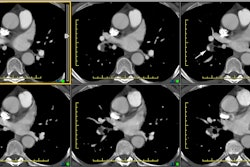
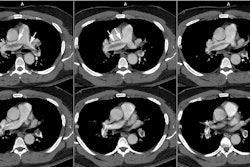
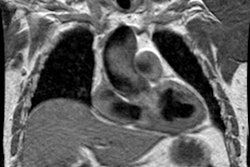
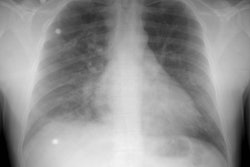
Pulmonary hypertension is the hemodynamic consequence of vascular changes within the precapillary (arterial) or postcapillary (venous) pulmonary circulation. These changes may be idiopathic, as in primary pulmonary hypertension or pulmonary veno-occlusive disease, but more commonly they represent a secondary response to alterations in pulmonary blood flow. The pulmonary and systemic bronchial circulations form broad anastomoses that largely prevent infarction except in settings of markedly elevated pulmonary venous pressure, underlying malignancy, or excessive embolic burden. Causes of precapillary pulmonary hypertension include long-standing cardiac left-to-right shunt, chronic thromboembolic disease, and widespread pulmonary embolism arising from intravascular malignant cells, parasites, or foreign materials. The classic radiologic features of precapillary pulmonary hypertension are central arterial enlargement, sharply pruned peripheral vascularity, and right-sided heart hypertrophy and chamber dilatation. Postcapillary pulmonary hypertension may develop secondary to focal venous constriction or to compromised pulmonary venous drainage due to left atrial neoplasia, mitral stenosis, or left ventricular failure. Radiologic manifestations of postcapillary pulmonary hypertension include prominent septal lines, small pleural effusions, and occasionally air-space opacities. In addition, radiologic evaluation of postcapillary pulmonary hypertension may demonstrate evidence of pulmonary arterial hypertension, secondary to the retrograde transmission of elevated pulmonary venous pressure across the capillary bed.
Publication Types:
Review
Review, tutorial