The first annotated dataset of anonymized COVID-19 medical images from the RSNA International COVID-19 Open Radiology Database (RICORD) has been published by the Cancer Imaging Archive (TCIA).
The lack of a diverse annotated dataset of COVID-19 images has hindered the capabilities of prediction models for the coronavirus, so earlier this year the RSNA launched RICORD with the goal of creating the largest open database of anonymized COVID-19 medical images in the world. It is freely available to the global research and education communities in order to help everyone gain new insights and apply tools such as artificial intelligence (AI) and deep learning, as well as accelerate clinical recognition of COVID-19.
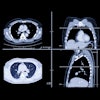
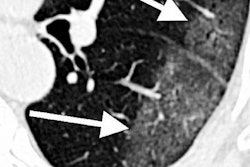
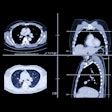
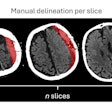
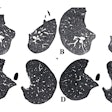
The initial dataset consists of 120 COVID-19-positive chest CT images from four international sites, provided with the aid of the Society of Thoracic Radiology and annotated by two teams of radiologists led by Dr. Scott Simpson of the University of Pennsylvania and Dr. Emily Tsai of Stanford University.
The dataset is the RSNA's first contribution to the Medical Imaging and Data Resource Center (MIDRC), a consortium for imaging and associated data. It was developed by the RSNA, the American College of Radiology, and the American Association of Physicists in Medicine. The resource center is funded by the U.S. National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering and hosted by the University of Chicago.
The RSNA COVID-19 AI Task Force will continue to update and expand upon the data available in RICORD with COVID-19-negative chest CT control cases in the pipeline, as well as a labeled set of 1,000 COVID-19-positive chest x-rays. An even larger set of CT and x-ray images has been submitted to RICORD and is currently being processed, the RSNA said.