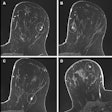
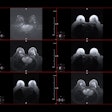
Using stress cardiac MRI in the emergency department observation unit can reduce hospital readmissions, coronary revascularization procedures, and the need for additional cardiac testing, according to a study published online May 8 by JACC: Cardiovascular Imaging.
Researchers from Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center, led by Dr. Chadwick Miller, executive vice chair of emergency medicine, recruited 105 patients with acute chest pain and randomized them to receive care either in the observation unit with cardiac MRI or in the hospital.
The patients were followed for 90 days, after which the researchers found significant reductions in coronary revascularization procedures, fewer hospital readmissions, and fewer recurrent cardiac testing episodes or the need for additional testing.
One limitation was the small, single-center scope of the study, according to Miller. The findings need to be replicated across multiple centers to be validated, he added.
The study builds on the team's previous research, which found that more complex patients managed in an observation unit with stress cardiac MRI testing had a reduction in care costs of about $2,100 per patient, per year.
The study was funded by the U.S. National Institutes of Health's National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute.


.fFmgij6Hin.png?auto=compress%2Cformat&fit=crop&h=100&q=70&w=100)
.fFmgij6Hin.png?auto=compress%2Cformat&fit=crop&h=167&q=70&w=250)