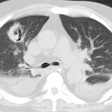
Fusariosis:
- Clinical:
Fusarium fungal species are being increasingly recognized as lethal pathogens in patients with hematologic malignancies [1]. The infection is typically acquired through the inhalation of airborne conidia that germinate and invade lung blood vessels in the setting of profound, sustained, immunosuppression [1]. Fusariosis has a worse outsome and fewer therapeutic options than Aspergillus infection [1]. Only high doses of liposomal amphotericin B and newer triazoles have been shown to be effective [1]. About 65% of patients die within one month of diagnosis [1].
- X-ray:
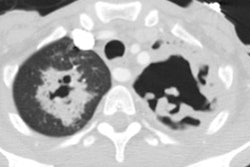
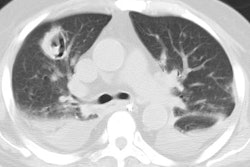
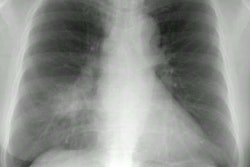
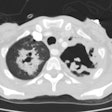
The CXR can appear normal in up to 25% of patients [1]. CT is abnormal in all cases [1]. Nodules or mass(es) are the most common CT finding (82% of patients) [1].
REFERENCES:
(1) AJR 2008; Marom EM, et al. Imaging of pulmonary fusariosis in patients with hematolgic malignancies. 190: 1605-1609