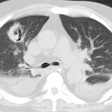
Chlamydia pneumoniae
Clinical:
Chlamydia pneumoniae is the third most common cause of community acquired pneumonia (after streptococcus and mycoplasma) [1] accounting for 6-12% of cases [2]. Chlamydia pneumoniae produces an "atypical pneumonia" [2]. The most common clinical presentation is sore throat, non-productive cough (usually for longer than 2 weeks), and fever [1]. COPD is a predisposing risk factor [2]. Complications such as meningitis or transverse myelitis are rare [2].
X-ray:
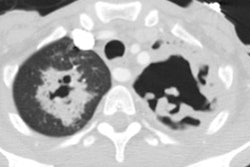
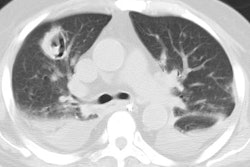
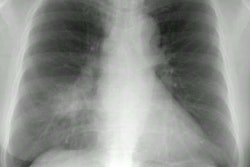
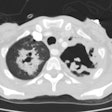
The most common CXR finding is airspace consolidation with interstitial infiltrates [1]. Findings on CT include lobular areas of consolidation, centrilobular/tree-in-bud nodules, and areas of ground glass attenuation [2].
REFERENCES:
(1) Radiol Clin N Am 2005; Tarver RD, et al. Radiology of community-acquired pneumonia. 43: 497-512
(2) Radiology 2006; Nambu A, et al. Chlamydia pneumoniae: comparison with findings of mycoplasma pneumoniae and streptococcus pneumoniae at thin-section CT. 238: 330-338