Herpes Simplex:
- Clinical:Herpes viruses (HSV) are a type of DNA virus which can remain dormant within host cells and reactivate at times of reduced host immunity [3]. Pneumonia is is uncommon, but predominantly caused by HSV type I and rarely by HSV type 2 [4].
Predisposing factors of HSV pneumonia include immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV), severe burns, organ transplantion, malignancy, and smoke inhalation [4]. Lower respiratory involvement with herpes is seen almost exclusively in immunocompromised patients after clinically evident mucocutaneous disease (ie: diagnosis of HSV pneumonia can be suspected in patients with associated oral and esophageal involvement). In organ transplant patients, the infection typically occurs in the first few months following transplant [3]. Patients typically present with dyspnea, cough, and fever [3]. Necrotizing tracheobronchitis can be seen in HIV patients with severe immune suppression. HSV penumonia responds to antiviral therapy in most cases [1].
- X-ray:
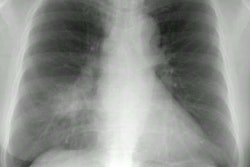
On CXR there
is usually non-specific, bilateral air space consolidation.
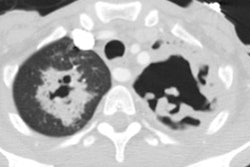
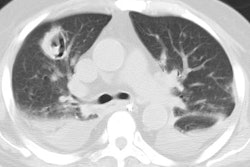
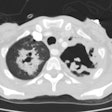
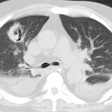
HRCT demonstrates predominantly multifocal or subsegmental areas of ground-glass attenuation and less domiant focal areas of consolidation [2,3,4]. HRCT may demonstrate the presence of diffuse, ill-defined nodules surrounded by areas of ground-glass attenuation ("halo" sign). Associated small pleural effusions are commonly found on both CXR and CT [3,4].
REFERENCES:
(1) J Thorac Imaging 1999; McGuinness G. Viral and pneumocystis infections of the lung in the immunocompromised host. 14: 25-36
(2) Radiographics 2002; Kim EA, et al. Viral pneumonias in adults: radiologic and pathologic findings. 22: S137-S149
(3) AJR 2005; Miller WT, Shah RM. Isolated diffuse ground-glass
opacity in thoracic CT: causes and clinical presentations. 184:
613-622
(4) Radiographics 2018; Koo HJ, et al. Radiographic and CT
features pf viral pneumonia. 38: 719-739