Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis: prediction at thin-section CT in patients with neutropenia--a prospective study.
Won HJ, Lee KS, Cheon JE, Hwang JH, Kim TS, Lee HG, Han J
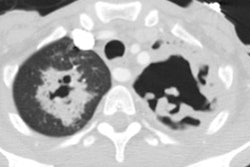
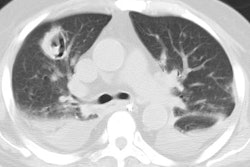
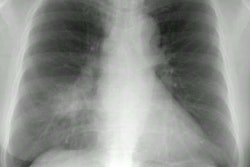
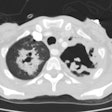
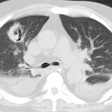
PURPOSE: To evaluate prospectively the usefulness of thin-section computed tomography (CT) in the prediction of biopsy-proved invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with neutropenia. MATERIALS AND METHODS: In 11 consecutively seen neutropenic patients, 12 open-lung biopsies were performed prospectively for suspected angioinvasive (n = 10) or airway-invasive (n = 2) pulmonary aspergillosis. Thin-section CT findings in the patients with angioinvasive pulmonary aspergillosis were reviewed, and the findings were compared with those of other diseases. RESULTS: Five of 12 biopsy specimens were positive for angioinvasive pulmonary aspergillosis; none was positive for airway-invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. In five (50%) of 10 cases, suspicion of angioinvasive pulmonary aspergillosis proved to be correct. The most common CT findings were segmental areas of consolidation plus ground-glass attenuation (four of five cases [80%]) and at least one nodule surrounded by a halo (two of five cases [40%]). Segmental areas of consolidation plus ground-glass attenuation were seen as isolated findings in three and mixed findings with nodules that have a surrounding halo in one case. In two patients, at least one nodule with a halo was an isolated finding in one patient and a mixed finding in one patient. Mucormycosis, organizing pneumonia, and pulmonary hemorrhage produced similar findings. CONCLUSION: At thin-section CT, segmental areas of consolidation plus ground-glass attenuation or at least one nodule with the halo sign were seen in patients with invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. The findings were nonspecific, however, and can be seen in neutropenic patients with mucormycosis, organizing pneumonia, or pulmonary hemorrhage.