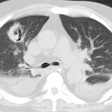
Malaria:
Clinical:
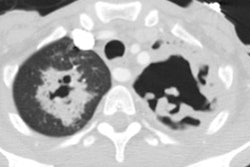
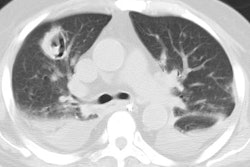
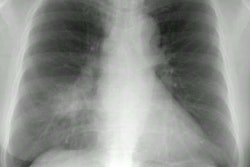
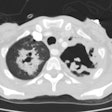
Only Plasmodium falciparum causes pulmonary disease and the infection is acquired from a mosquito bite, blood transfusion, or I.V. drug use. Pulmonary involvement occurs in only 3 to 10% of infected patients. Fever with chills, sweating, anemia, leukopenia, and splenomegaly are the most common clinical findings [1]. Pulmonary involvement may produce minimal upper airway complaints to fatal pulmonary edema (ARDS). Treatment consists of quinine.
X-ray:
Less severe pulmonary involvement may produce very few findings on CXR. Pleural effusion or interstitial infiltrates may occur. Severe disease can produce a radiographic appearance similar to pulmonary edema.
REFERENCES:
(1) Radiographics 2005; Martinez S, et al. Thoracic manifestations of tropical parasitic infections: a pictoral review. 25: 135-155