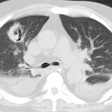
Opportunistic fungal pneumonia.
Connolly JE Jr, McAdams HP, Erasmus JJ, Rosado-de-Christenson ML
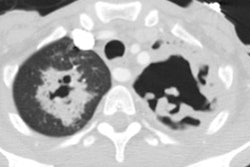
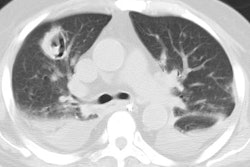
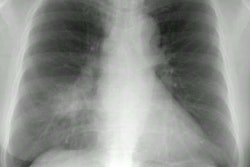
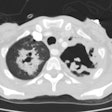
Opportunistic fungal infection is a common cause of serious morbidity
and mortality in immunocompromised patients. These infections occur primarily
in patients with chemotherapy-induced neutropenia, acquired immunodeficiency
syndrome. or immunosuppression after solid organ or bone marrow transplantation.
The most important opportunistic fungal pathogens include Cryptococcus
neoformans, Candida and Aspergillus species, and the fungi that cause mucormycosis.
Opportunistic pneumonia caused by previously unrecognized pathogens, such
as Fusarium, Penicillium, and the dematiaceous fungi, are increasingly
reported. The clinical and radiologic features of opportunistic fungal
pneumonia are highly variable and often nonspecific. Diagnosis requires
knowledge of the various modes of presentation, radiologic manifestations,
and epidemiology of these infections. Because many of these organisms can
colonize the upper airway, sputum cultures are considered diagnostically
unreliable. Instead, definitive diagnosis requires culture of the fungus
from infected tissue or demonstration of the organism on microscopic examination.
Review
Review, tutorial
PMID: 9894953, UI: 99110244