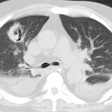
Rhodococcus equi:
Clinical:
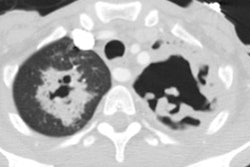
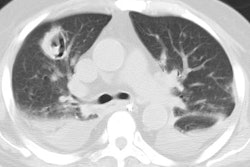
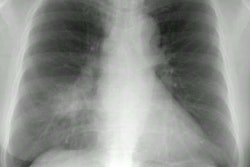
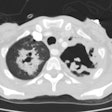
Rhodococcus equi pneumonia is a zoonosis that occurs rarely in immune compromised patients with AIDS. Patients usually present with an indolent course of cough, fever, and dyspnea [3]. The pneumonia frequently cavitates and may cause empyema, extra-pulmonary abscesses, and mediastinal invasion. Associated bacteremia is common. Although the infection is often indolent, it is characterized by frequent antibiotic failure and relapse. The infection may occur in patients exposed to horses or other farm animals.X-ray:
Radiographic findings include single or multiple segmental or lobar infiltrates- predominantly in the upper lobes, which are often cavitary and associated with pleural effusion or empyema. Additional features may include adenopathy.REFERENCES:
(1) Radiologic Clinics of North America 1997; McGuinness G. Changing trends in the pulmonary manifestations of AIDS. 35 (5): 1029-1082
(2) J Thorac Imaging 1998; Haramati LB, et al. Approach to the diagnosis of pulmonary disease in patients infected with the human immunodeficiency virus. 13: 247-260
(3) AJR 2003; Brecher CW, et al. CT and radiography of bacterial respiratory infections in AIDS patients. 180: 1203-1209