Legionella:
Clinical:
Legionella is a gram negative, weakly acid fast bacillus, but it can be identified with a silver impregnation stain. The reservoir for the organism is water and the organism is resistant to heat (it proliferates best in warm water). There are endemic and sporadic forms of infection. Outbreaks can result from contaminated air conditioning systems, cooling towers, hot water storage tanks, and shower heads [1]. The infection usually affects the immunocompromised, patients with COPD, or alcoholics. Patients frequently have extra-pulmonary symptoms such diarrhea, myalgias, elevated LFT's, encephalopathy, and renal dysfunction.X-ray:
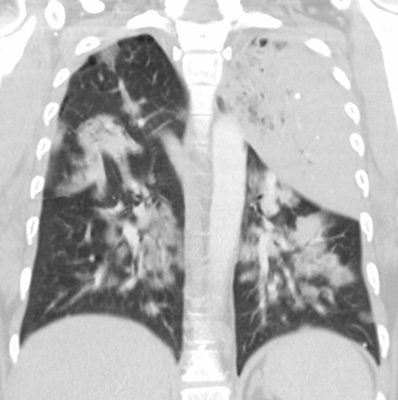
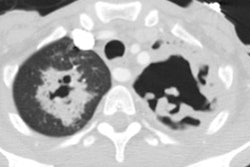
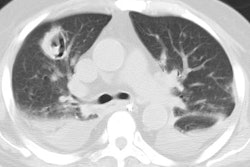
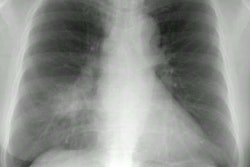
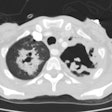
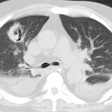
The infection usually begins as an area of peripheral patchy airspace disease that progresses to a consolidative pattern. Bilateral involvement occurs in up to 50% of cases. Pleural effusions frequently develop during the course of the illness (up to 50% of cases [2]). Adenopathy and cavitation is rare. The radiographic abnormalities can be slow to clear following initiation of therapy.
Legionella pneumonia on CT: Bilateral, multilobar airspace consolidations in a patient with Legionella pneumonia. |
|
REFERENCES:
(1) J Thorac Imaging 1998; Conces DJ. Bacterial pneumonia in immunocompromised patients. 13: 261-270
(2) Radiol Clin N Am 2005; Tarver RD,
et al. Radiology of community-acquired pneumonia. 43: 497-512