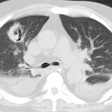
Mediastinal tuberculous lymphadenitis: CT findings of active and inactive disease.
Moon WK, Im JG, Yeon KM, Han MC
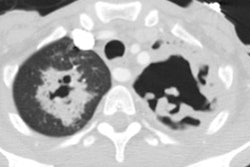
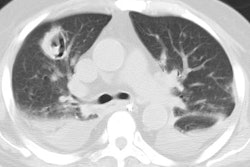
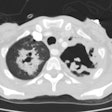
OBJECTIVE: The purpose of this study was to analyze CT findings of active and inactive disease in patients with mediastinal tuberculous lymphadenitis. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Using biopsy and culture results, we categorized 49 consecutive patients with mediastinal tuberculous lymphadenitis studied with CT scans as patients with active disease (n = 37) or patients with inactive disease (n = 12). Follow-up CT scans were obtained after antituberculous therapy in 25 patients with active disease and three patients with inactive disease. In 10 patients (seven with active disease and three with inactive disease), CT findings were analyzed and correlated with pathologic findings. RESULTS: In all 37 patients with active disease, the nodes (n = 151) varied in size (1.5-6.7 cm; mean, 2.8 +/- 1.0 cm) and had central low attenuation and peripheral rim enhancement. Calcifications within the nodes were seen in seven patients (19%). In the 12 patients with inactive disease, the nodes (n = 34) varied in size (1.0-4.7 cm; mean, 2.1 +/- 1.0 cm) but were usually smaller than nodes in patients with active disease. In the patients with inactive disease, the diseased nodes were homogeneous and without low-attenuation areas. Calcifications within the nodes were seen in 10 (83%) of the 12 patients with inactive disease. Low-attenuation areas within the nodes corresponded pathologically to areas of caseation necrosis in seven patients with active disease and in no patients with inactive disease. After treatment, enlarged mediastinal nodes in patients with active disease shrunk and low-attenuation areas within the nodes disappeared in all 25 patients. However, the findings of calcified nodes in the three patients with inactive disease did not change after 6 months of follow-up. CONCLUSION: In these 49 patients with mediastinal tuberculous lymphadenitis, CT findings of nodes with central low attenuation and peripheral rim enhancement suggested active disease, and findings of homogeneous and calcified nodes suggested inactive disease. Low-attenuation areas within the nodes had pathologic correspondence to areas of caseation necrosis and may be a reliable indicator for disease activity.