Approach to the diagnosis of pulmonary disease in patients infected with the human immunodeficiency virus.
Haramati LB, Jenny-Avital ER
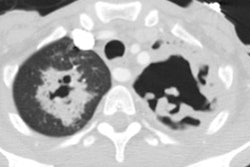
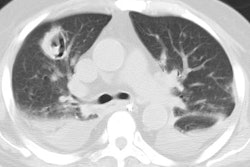
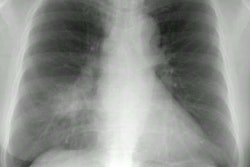
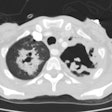
Patients infected with the human immunodeficiency virus are predisposed to develop a variety of common and uncommoninfectious and neoplastic pulmonary diseases. Clinical information that can stratify the risk of occurrence of these pulmonaryconditions includes: 1) CD4 cell count-the most important determinant; 2) concurrent antimicrobial therapy; 3) prior travelhistory; 4) known latent infections that may reactivate: and 5) underlying respiratory disease. Specific pulmonary diseases are discussed including: bacterial pneumonia, bronchitis, mycobacterial and fungal infections, pneumocystis carinii pneumonia,toxoplasmosis, cytomegalovirus, Kaposi sarcoma, lymphoma, and lung cancer. A differential diagnosis can be generated basedon the chest radiographic pattern. Focal or multifocal areas of consolidation usually represent conventional bacterial pneumoniaor, less commonly, tuberculosis. In severely immunocompromised patients, unusual diseases causing consolidation should beconsidered including: Rhodococcus infection, nocardiosis, cryptococcosis, aspergillosis, and lymphoma. Nodules can bepresent in tuberculosis, histoplasmosis, cryptococcosis, and Kaposi sarcoma. Interstitial opacities are common in pneumocystiscarinii pneumonia, histoplasmosis, and cytomegalovirus pneumonia. Cavitation and cysts are features of pneumocystis cariniipneumonia, tuberculosis, aspergillosis, and lung cancer. Disease of the airways is increasingly recognized in those with acquiredimmunodeficiency syndrome. Lymphadenopathy is most common in mycobacterial infection, but can be a feature of fungalinfection, lymphoma, Kaposi sarcoma, and lung cancer. The combined use of clinical information, knowledge of typical conditions associated with the human immunodeficiency syndrome, and radiographic patterns offers a useful approach to the diagnosis of pulmonary disease in the patient with the human immunodeficiency virus.